Which Cell Lacks A Nucleus
No Nucleus? No Problem: Red Blood Cells and Platelets
Red blood cells and platelets

1. Carmine blood cells take vii days to develop from stem cells called hemocytoblasts.
Hemocytoblasts, or multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, give rise to myeloid stem cells, which differentiate into myeloblasts, megakaryocytes, and carmine blood cells (erythrocytes). Cherry-red blood cell production is regulated by the hormone erythropoietin, which is produced by cells in the kidneys and liver.
Mature crimson blood cells are flexible, oval or round biconcave discs that motility hands through the claret vessels. Certain pathologies, such as sickle-cell anemia, alter the shape and flexibility of carmine claret cells, making information technology difficult for them to movement smoothly through blood vessels.
Unlike most other eukaryotic cells, mature red blood cells don't have nuclei. When they enter the bloodstream for the commencement fourth dimension, they eject their nuclei and organelles, so they tin can carry more hemoglobin, and thus, more oxygen.
Each red claret cell has a life span of around 100–120 days. Old, dead, or damaged crimson blood cells are engulfed past phagocytic cells in the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. The atomic number 26 from these cells is afterwards recycled to produce new hemoglobin.
two. Ruby-red blood cells produce a protein called hemoglobin, which helps them carry out their primary function—transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues.
Hemoglobin is the protein that makes it possible for red claret cells to carry oxygen. Each molecule of hemoglobin is made up of four protein chains. Each chain has a heme group that contains an iron atom. Oxygen tin can bind to these iron atoms, which means that one molecule of hemoglobin can comport iv oxygen molecules. The bond between oxygen and the fe independent in hemoglobin'due south heme groups is what makes oxygenated blood red.
In the lungs, the hemoglobin in the red blood cells picks up oxygen. And so, the heart pumps the oxygenated blood out through the aorta, moving it through arteries and capillaries to reach the body's tissues.
After the hemoglobin releases its oxygen molecules into the body's tissues, it can class bonds with some of the carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed into the bloodstream. However, hemoglobin does not carry all the carbon dioxide in the blood dorsum to the lungs—the claret tin also transport CO2 every bit a dissolved gas or as bicarbonate (HCO3).
When inhaled, carbon monoxide (CO) binds to hemoglobin's heme groups. When this happens, information technology prevents oxygen from binding to the heme groups, and therefore, the hemoglobin can't carry oxygen to the body's tissues. As a result, carbon monoxide poisoning tin crusade permanent damage to the brain and/or heart, and information technology can be fatal.
3. Inactivated platelets are irregular disc-shaped structures. Activated platelets are round with projections.
Like red blood cells, platelets are derived from myeloid stem cells. Some of these stalk cells develop into megakaryoblasts, which give ascension to cells called megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. After a megakaryocyte has matured, pieces of its cytoplasm intermission away into cell fragments called platelets. A single megakaryocyte can produce 1000–3000 platelets. Because they are not cells, platelets don't have their ain nuclei. However, they do incorporate numerous granules (or vesicles).
The hormone thrombopoietin, produced by the liver and kidneys, regulates the production of megakaryocytes and platelets.
Platelets have dissimilar appearances in their inactivated and activated states. When inactivated, platelets are irregularly shaped discs. Activated platelets are spherical, with protrusions that allow them to stick to wound tissue and to other platelets to class a plug at the site of a blood vessel tear. Activated platelets too release chemicals from their granules to initiate clotting.
The life span of a platelet is about 10 days. Similar scarlet claret cells, one-time platelets are phagocytosed. Reserve platelets are stored in the spleen.
4. Platelets dodder at sites of injury to prevent blood loss.
When a blood vessel tears, platelets adhere to the (damaged) blood vessel wall virtually the tear, forming a platelet plug. At this point, they modify from their inactive to their active shape, and they empty the contents of their granules.
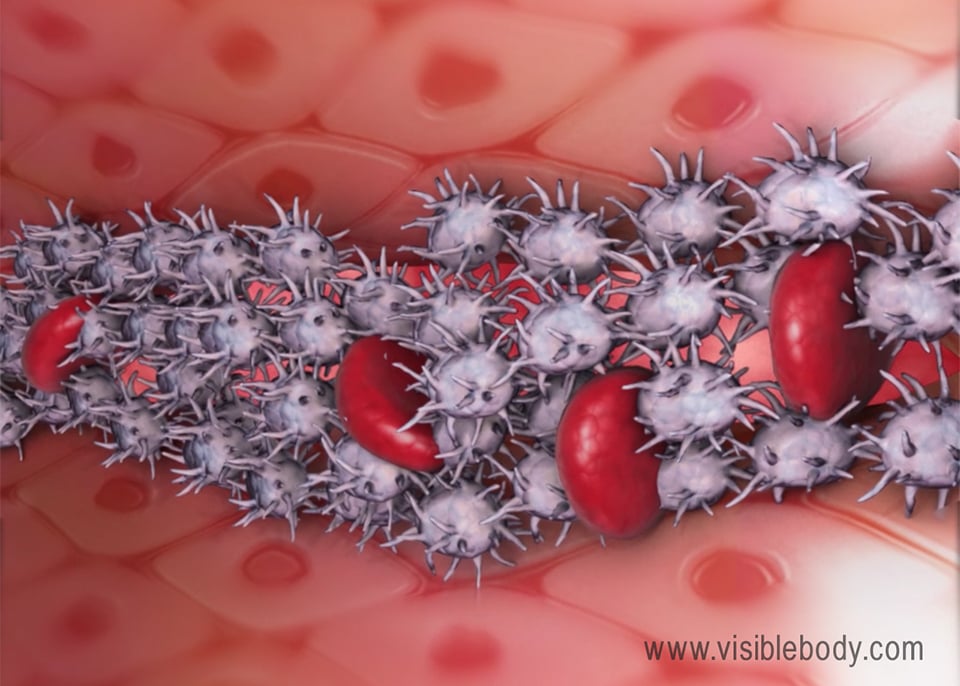
At the site of an injury, the platelets connect to one another and release chemicals that stimulate blood clotting. Proteins called clotting factors class fibrin threads that, together with the platelets, form a jell.
Which Cell Lacks A Nucleus,
Source: https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/biology/blood-cells/red-blood-cells-platelets
Posted by: smithwitheoper.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Cell Lacks A Nucleus"
Post a Comment